Server Virtualization Small Business
Server Virtualization
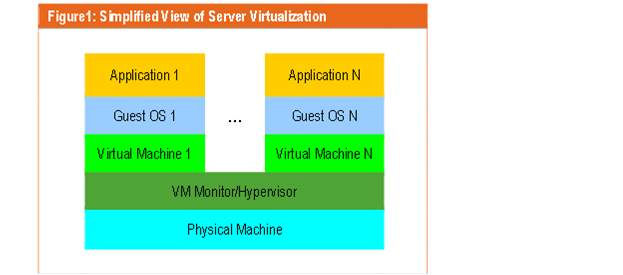
Server virtualization is a tangible, physical infrastructure in a local environment where multiple servers are able to operate on the same one machine, or hardware. As a result, this now one, single host server controls access to all resources and multiple servers located on it. Many businesses who invest in virtualization to store, access, and secure the majority of their data also embrace the use of cloud computing to maximize the IT services it provides. Unlike virtualization, cloud computing is an intangible product ~ a service; it remotely controls and interacts with all the applications and data stored on your server. As a System's Administrator or other IT personnel at your company, you are the expert your staff, colleagues, and stakeholders defer to when problems arise. Here’s some things to consider when considering implementing server virtualization at your company:
Advantages of virtualization:
- conserves physical space by consolidating hundreds (or thousands) of servers into one server running multiple virtual environments
- provides a way to run the same application on multiple servers (redundancy) without having to purchase additional hardware
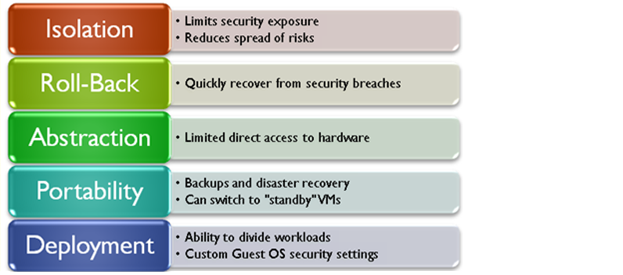
- creates isolated, independent systems for you to test new applications or operating systems without worrying about affecting other applications or having to buy a dedicated physical machine to run tests
- permits the movement (migration) of a virtual server from one physical machine in a network to another
- centralized storage that prevents theft, damage, or loss of critical data
- reduces expenses by eliminating the need to: buy additional individual dedicated servers to get more computing power, pay staff overtime or hire additional staff to maintain multiple servers. Further cost savings are experienced by: a reduced utility/energy bill, an increase in available physical square footage workspace, and a tax break for creating less of a carbon footprint
- if at all, only one application on one operating system can be affected by an attack vs. the whole system
Disadvantages of virtualization:
- divides up the processing power among all the virtual servers and makes those servers dedicated to applications with high demands on processing power run slower
- the system could crash if the server can't meet processing demands
- the more virtual machines a physical server must support, the less processing power each server can receive
- too many virtual servers could impact the server's ability to store data
- can only migrate a virtual server from one physical machine to another (and only if both physical machines use the same manufacturer's processor)
- if migration isn't an option, then all the applications running on the virtual servers hosted on the physical machine will be unavailable during maintenance
Training
While your company may seek a third-party IT consulting firm to assist with the build of the virtual environment and initial migration, you’ll want to ensure you and your team are proficient in the daily operations of managing the various facets of your company’s environment. You can’t afford to learn through trial and error; it requires understanding acquired through specialized certifications. Whether you and your team complete certification training before your company’s IT infrastructure goes virtual or during implementation, it’s important to complete the certification training.
Security
In an October 2014 article published by Business Wire, the growing concern of security in virtualized environments was addressed. “The majority of organizations are still using the same tools for their virtualized environments - such as antivirus and firewalls - as they did for their in-house physical machine set-ups…[these] fail to address the dynamic nature of the virtualized environment, and cannot track policies to virtual machine creation or movement,” explained ABI Research staff member, Christine Gallen.
A November 2014 article on PRNewswire shared the results from a Security Monitoring Study on priorities and challenges for information security in 2015; the results of the study were based on the responses from 145 IT decision makers in various industries. Only 15% of the participants said they felt well-prepared and trained for security threats in today’s virtualized and cloud computing world. "IT pros are looking beyond basic compliance and beginning to focus on security best practices to get out in front. Defining and implementing an effective security program that provides both proactive and reactive security monitoring on a continuous basis and is supported by trained security professionals, who can engage in timely analysis and remediation, is mandatory in protecting businesses against current threats," said Brian Mehlman, Vice President of Product Management, EiQ Networks.
Lessons learned
Here is a compilation of value lessons learned, recommendations and tips from those whom have already embraced virtualization:
- become well-versed in everything IT-related, from new advances in technology to certifications available to acquire expertise in this new process
- be able to relate to the decision-makers (money holders) on their level; typically, they’ll have zero knowledge of technology, help them understand (if even in layman’s terms) the necessity for virtualization
- research the different hardware and software options
- identify support resources to help with the migration and maintenance of your new virtual environment
- complete the recommended certifications to help you become confident in maintaining the environment
- gather lots of data regarding your current local physical servers, including: performance trends, alerts, server efficiency (or lack thereof), downtime numbers
If are you interested in becoming a specialist in Virtualization, the following certifications are currently available on our Public Schedule:
CompTIA: Storage+ Powered by SNIA, Cloud+
Microsoft: 10215 Implementing and Managing Server Virtualization, 10324 Implementing & Managing Microsoft Desktop Virtualization